[最も欲しかった] nasal sinuses anatomy 146043-Nasal cavity anatomy
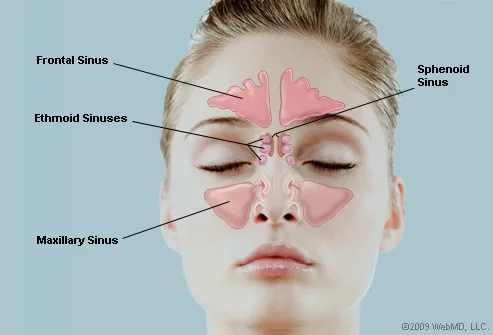
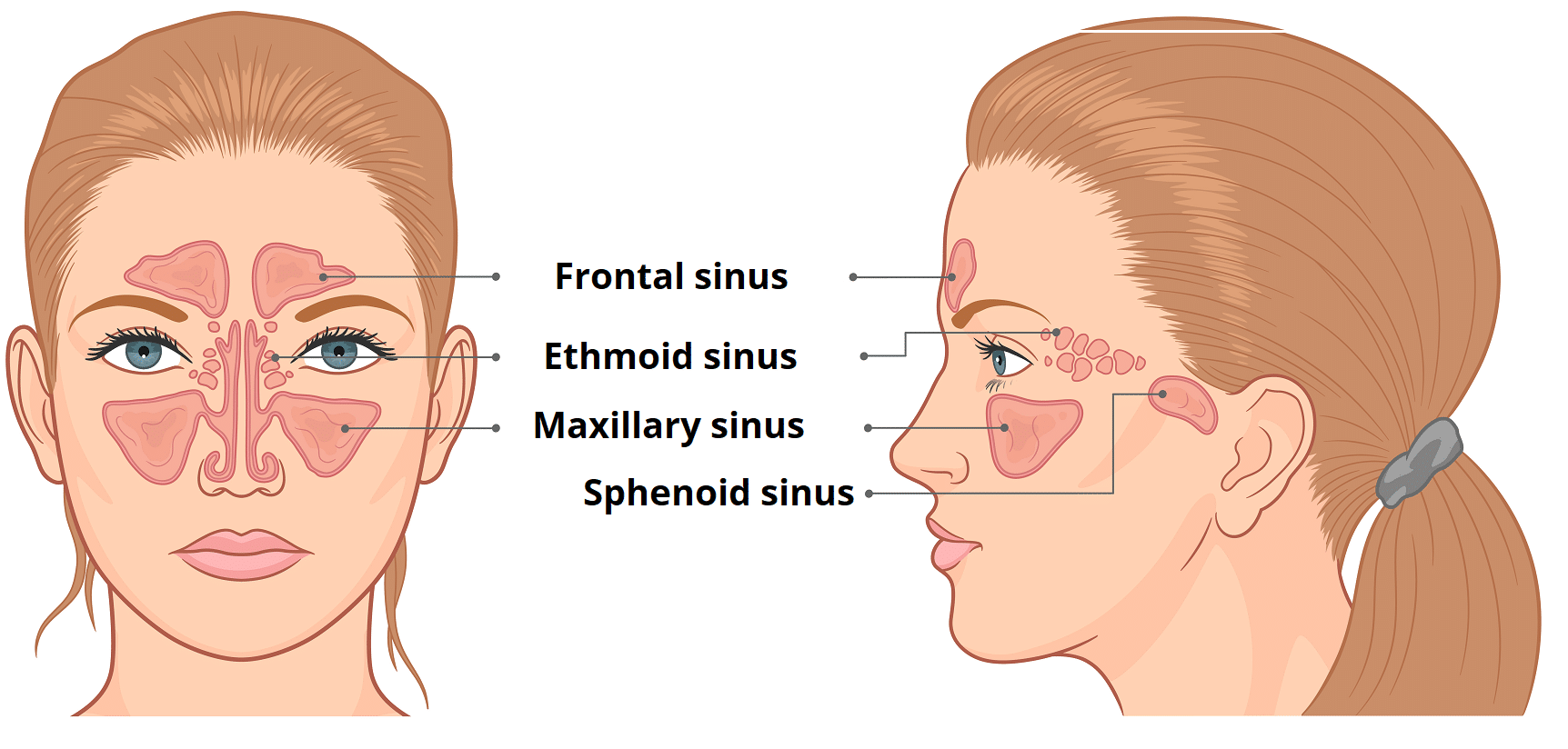
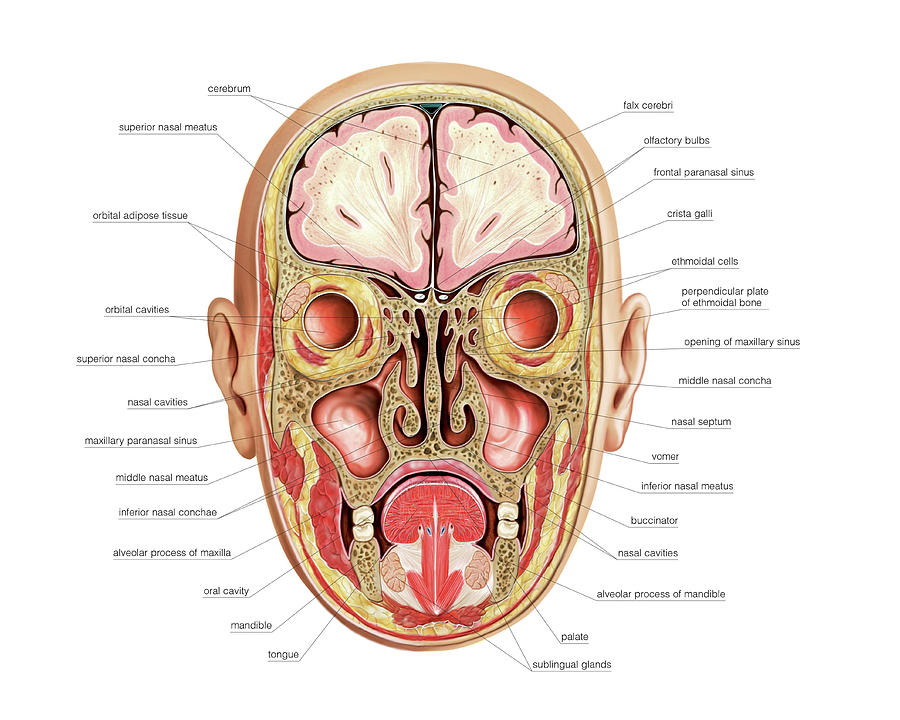
· Airfilled cavities located within specific facial and skull bones are known as paranasal sinuses Humans have four paired paranasal sinuses, frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, and ethmoid, all extending from the respiratory area of the nasal cavity, and named after the bones they are found inAnatomy Furuncle of the nose Cause •Skin infection of the nasal vestibule / tip of the nose Usually due to hair follicle Symptoms •Swelling, Pain, Redness Danger •Septic emboli via the angular vein / cavernous sinus drainageParanasal Sinuses Paranasal sinuses refer to a group of airfilled spaces around the nasal cavity (a system of air channels that connect the nose with the back of the throat) (1)They facilitate the circulation of the air breathed in and out of the respiratory system (2) Paranasal sinuses have four different pairs maxillary sinuses, frontal sinuses, sphenoidal sinuses, and ethmoidal
What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities
Nasal cavity anatomy
Nasal cavity anatomy-Ogle OE, Weinstock RJ, Friedman E Surgical anatomy of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 12; Parker NP, Pearlman AN, Conley DB, et al The dilemma of midline destructive lesions a case series and diagnostic review Am J Otolaryngol 10; Schwarz JN, Donnelly EH, Klintworth GK OcularNose and paranasal sinuses is presented through a discussion of the important structures of this complicated region A correlation with intricate endoscopic topo graphical anatomy is discussed for a clear understanding of the nasal cavity and its relationship to adjoining sinuses and danger areas A threedimensional anatomy is complemented with schematic diagrams Developmental Anatomy




Nose Sinus Ent
· The lymphatic drainage occurs in the same way as the posterior ethmoid sinus The posterior ethmoidal artery and the posterior lateral nasal branches supply the sphenoidal sinuses The posterior ethmoidal nerve and the orbital branch ofThe sinuses are cavities, or airfilled pockets, near the nasal passage As in the nasal passage, the sinuses are lined with mucous membranes There are 4 different types of sinuses Ethmoid sinus This sinus is located inside the face, around the area of the bridge of the nose It is present at birth, and continues to growThe ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located
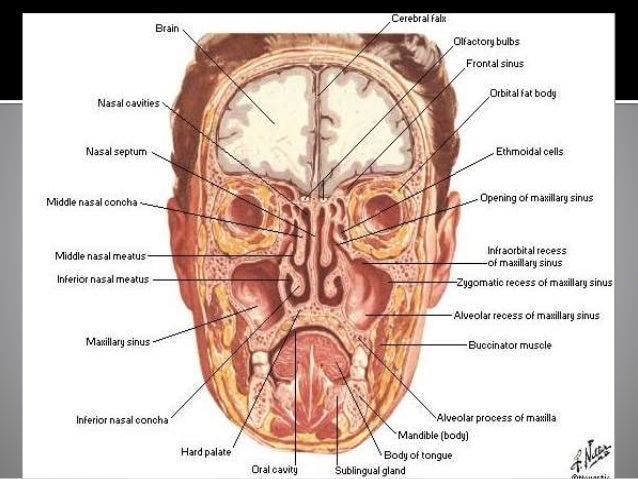
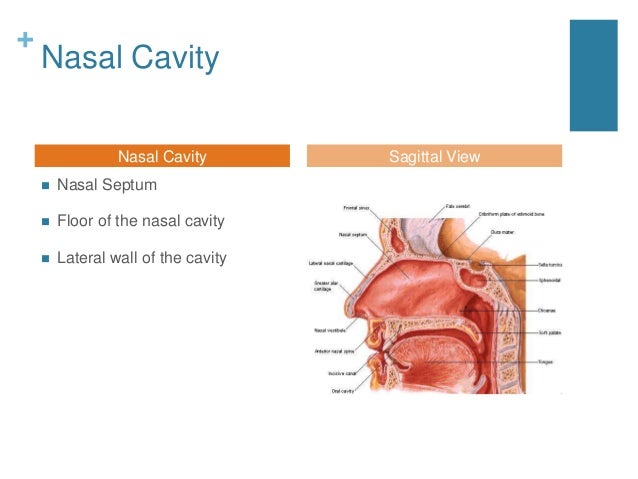
· 2 Anatomy of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Carolina Martins, Luiz Felipe de Alencastro, Alberto Carlos Capel Cardoso, Alvaro Campero, Alexandre Yasuda, Jian Wang, Luiz Carlos de Alencastro, and Albert L Rhoton, Jr Tips and Pearls • The nasal cavity is a natural pathway to the anterior cranial fossae, orbit, pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossae, · The NoseThe nose consists of the external nose and the nasal cavity, Both are divided by a septum into right and left halves 3 · Sinus Anatomy – Four Pairs of Sinuses Human beings have four pairs of sinuses Around 10% don't develop frontal sinuses However, this does not have any impact on their health and usual activities Let's now talk about the first pair of sinuses located in the nasal cavities Known as maxillary sinuses, they are placed behind the
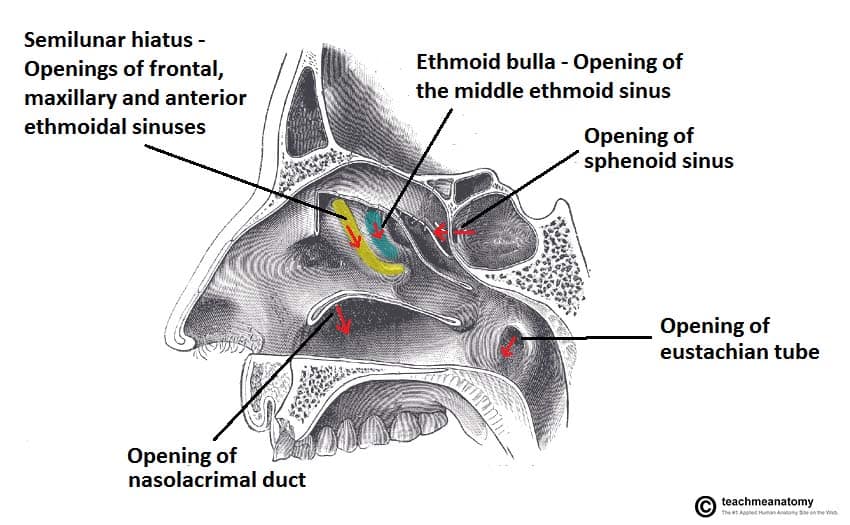
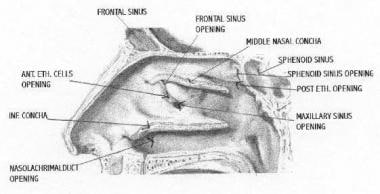
· In bones behind your nose are your sphenoid sinuses They're lined with soft, pink tissue called mucosa Normally, the sinuses are empty except for a thin layer of mucus1305 · ) are airfilled cavities within the bones of the skull that surround the nasal cavity The nose and the paranasal sinuses provide resonance to the voice and humidify and warm inhaled air The nasal cavity consists of a respiratory region, which is lined with ciliatedSchematic anatomy of the sinuses The sinuses can be subdivided into two groups, depending where they drain into The anterior ethmoid cells, the frontal sinus and maxillary sinus drain into the middle meatus The posterior ethmoid cells and sphenoid sinus drain into the superior meatus The nasolacrimal duct drains into the inferior nasal meatus Maxillary sinus The first sinus to be




What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities




Anatomy Of The Para Nasal Air Sinuses Dr Yusuf Youtube
Nasal and paranasal sinus anatomy and physiology Clin Allergy Immunol 07; Author Fuad M Baroody 1 Affiliation 1 Department of Surgery, Section of OtolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery, Pritzker School of Medicine, University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois, USA PMID No abstract availableFrontal sinus, sphenoidal sinus,; · Surrounding the nasal cavities are aircontaining mucosal lined sinuses, which include the frontal sinuses (superior anterior), ethmoid sinuses (superior), paired maxillary sinuses (lateral), and sphenoid sinuses (posterior) All of these paranasal sinuses, except the sphenoid, communicate with the nasal cavity via ducts that drain through ostia, which empty into spaces



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Pin On Medical Illustration Animation
· Ethmoid sinuses The ethmoid sinuses are located in the ethmoid bone, which separates the nasal cavity from the brain These sinuses aren't single sacs but a collection of 6 to 12 small air cellsBlood supply small arteries from the facial, maxillary, infraorbital and greater palatine arteries; · 2 Endoscopic Anatomy of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses Anatomical textbooks and atlases offer very accurate descriptions of the structure and topography of the nose and the paranasal sinuses, but the details have been worked out from macroscopic laminar sections on cadaver dissections However, intranasal surgeons must be able to orientate themselves looking




Paranasal Sinus Definition Location Anatomy Function Picture



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy
The anatomy of the nose and paranasal sinuses can be quite complex The nose have two nasal passages that are divided by the nasal septum Both nasal passages have inferior, middle, and superior (and sometimes another called "supreme") turbinates that severe multiple purposes, including direction of airflow, filtration, and sense of smellDefinition of Nasal Sinuses Nasal sinuses are hollow, airfilled spaces, within the bones of the skull and face We possess four pairs of sinuses Each sinus connects to the nasal cavity through small openings called ostium Each sinus is named for the bone within which it is located · This eAnatomy module contains 105 illustrations dedicated to the anatomy of the nose, the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses These fully annotated anatomical illustrations are presented as a comprehensive atlas of the nasal cavity, specially designed for medical students, medicine residents and healthcare professionals Material and methods




Anatomy Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Flashcards Quizlet



The Anatomy Of The Nose Dummies
09 · It is divided in the midline by the nasal septum On each side, it is flanked by the maxillary sinuses, and roofed by the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses, in an anterior to posterior fashion While seemingly simple, sinonasal anatomy is composed of intricate and subdivided air passages and drainage pathways that connect the sinuses1 Anatomy and Physiology of the Maxillary Sinus Harold A DeHaven, Jr CHAPter 1 Anatomy of the maxillary sinus The maxillary sinus is the largest of the four bilateral airfilled cavities in the skull It is located in the body of the maxilla and is a pyramidalshaped structure having as its base the medial wall (the lateral nasal wall) ThisThe sinuses make the facial bones lighter, and establish the adult contour of the face 4 The mucus secretion of the sinuses is drained into the meatuses of the nose (except the inferior meatus) partly by the movements of ciliated epithelium and partly by the suction created by negative air pressure of the nasal cavity
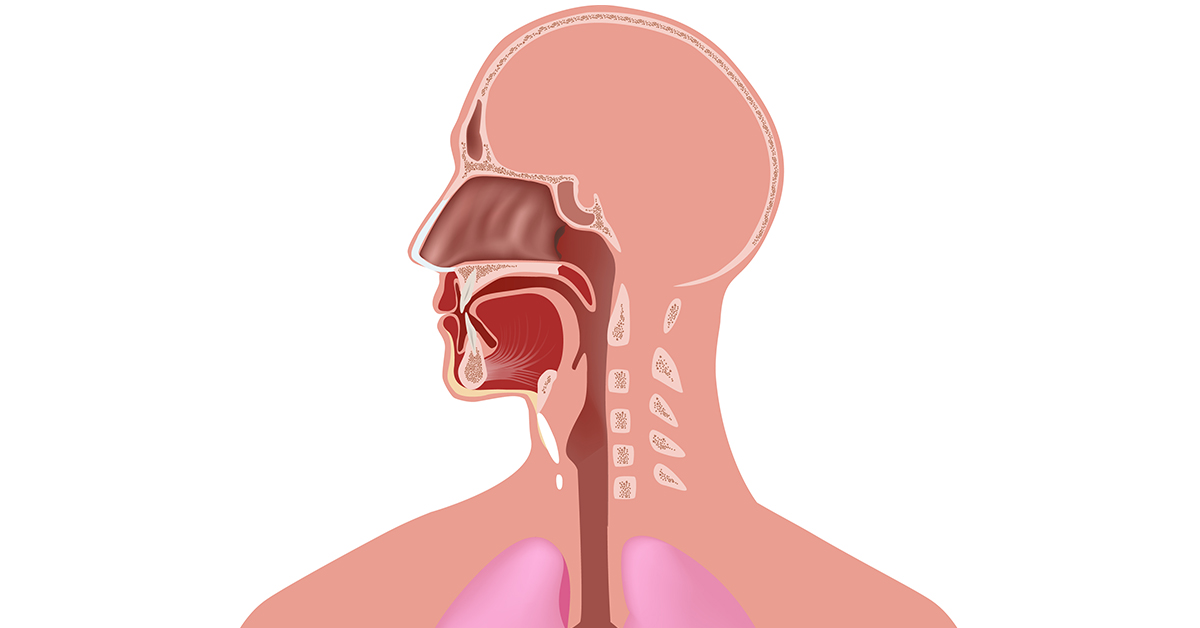



Baton Rouge Nasal Sinus Anatomy Ent Specialists Of Louisiana



Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Structure And Function Organization Of The Respiratory System
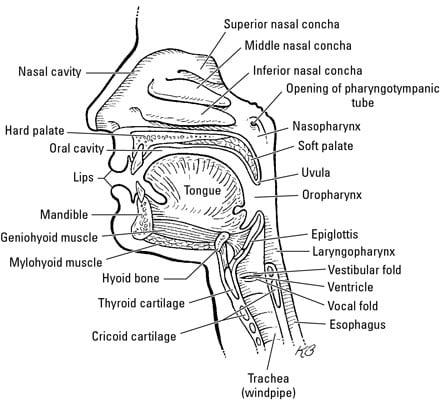
Where do I get my information from http//armandohorg/resourceFacebookhttps//wwwfacebookcom/ArmandoHasudunganSupport me http//wwwpatreoncom/armando · Nasal Cavity Definition The nose is one of the primary sensory organs responsible for the sense of smell, while it also plays major roles in respiration and speech production 1The nasal cavity lies just behind the two nostrils and forms the interiors of the nose It makes up the upper respiratory system along with the paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx 2, and isThe paranasal sinuses usually consist of four paired airfilled spaces They have several functions of which reducing the weight of the head is the most important Other functions are air humidification and aiding in voice resonance They are named for the facial bones in which they are located maxillary sinus;



1




Clinical Anatomy Of The Nose Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Johannes Lang Amazon Com Books
Ethmoid sinus (known as ethmoidal air cells)•Nasal Fontanelles » divided (arbitrarily) by the projection of the uncinate over its surface •posterior (superior)= accessory ostia of the maxillary sinuses •anterior (inferior) = maxillary ostiumA sinus is a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue In common usage, "sinus" usually refers to the paranasal sinuses, which are air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose and connecting to it




Medical Illustrations Gallery Cancer Net
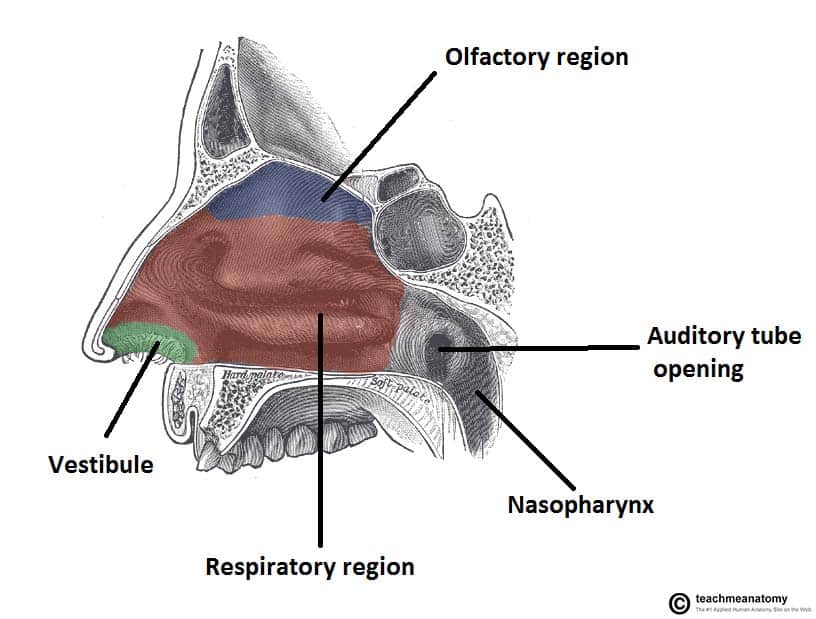



The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation Teachmeanatomy
Summary location paired sinuses within the body of the maxilla;The paranasal sinuses (latin sinus paranasales) are four bilateral airfilled spaces within bones of the skull surrounding the nasal cavityFour bones of the skull each accommodates a pair of paranasal sinuses that are named according to the bone in which they are locatedThe four sinuses are maxillary sinus,;Innervation superior alveolar, greater palatine and infraorbital nerves;




Nose And Sinus Anatomy Dr Thomas S Higgins Md Msph




Atlas Of Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses Paranasal Sinuses
Nasal & Sinus Anatomy FAQ If you're considering undergoing sinus surgery relating to conditions of the nasal cavity and sinuses that you may be suffering from, our expert sinus surgeons encourage you schedule an initial consultation with us to learn more Below are some of the most frequently asked questions relating to our nasal cavity and sinuses, including but not limited toThe frontal sinuses are above the eyes;07 · /b Sinonasal Anatomy Introduction This section focuses on sinonasal anatomy, beginning with schematic construction of the ethmoid complex For many paranasal sinus surgeons, initial understanding of the ethmoid sinuses proves challenging Simplified methodological construction of the ethmoid sinuses and surrounding structures will
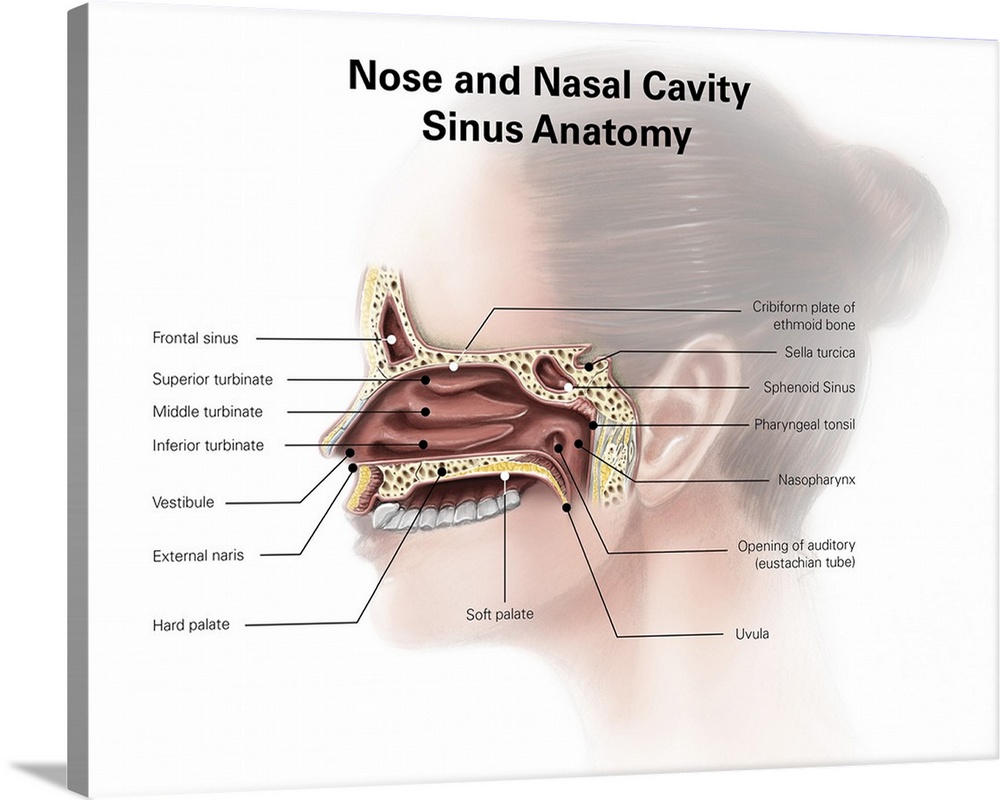



Digital Illustration Of Nose And Nasal Sinus Anatomy Wall Art Canvas Prints Framed Prints Wall Peels Great Big Canvas
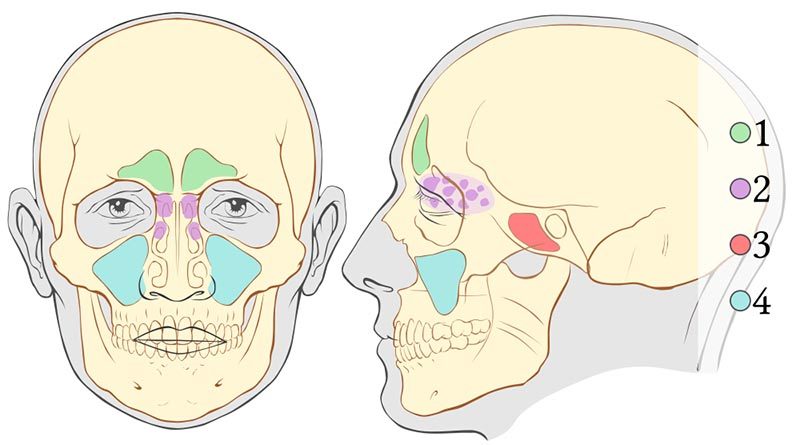



Sinus Barotrauma Divers Alert Network
0509 · Sinus and nasal cavity anatomy The sinus is lined with a membrane called the Schneiderian membrane, which has ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells that produce mucus on the internal side, and periosteum on the osseous side (the side with bone) In the maxillary sinus there is also an opening called the maxillary ostium (or the maxillary hiatus), · An interactive quiz covering the Paranasal Sinuses of the Nasal Cavity through multiplechoice questions and featuring the iconic GBS illustrations More Skeletal System · Next Anatomy of the Nose Nasal Airflow Air flows superiorly into the nares, determined by its position and the anterior nasal valve The airstream then turns posteriorly approximately 90° and flows into the nasopharynx The airstream then turns inferiorly 90° through the pharynx and larynx and flows into the trachea toward the lungs



Paranasal Sinuses Human Anatomy Organs
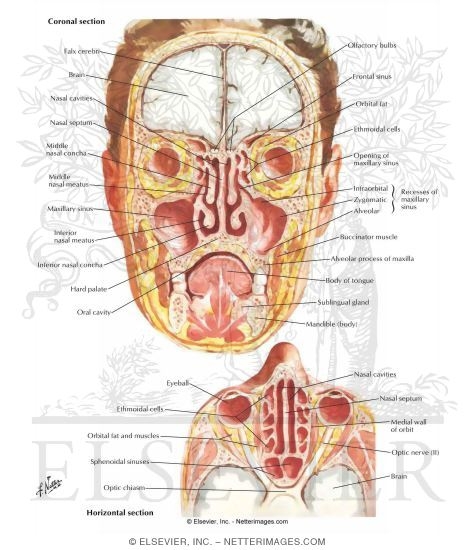



Paranasal Sinuses Nasal Allergy
Gross anatomy Described as a pyramid, the maxillary sinuses have a base on the lateral border of the nose, with the apex pointing towards the zygomatic · Anatomy of nose and paranasal sinuses 1 ANATOMY OF NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUSES DEPT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY PI M S 2 NOSE ANATOMY DEVELOPMENT Nose develops from frontonasal process which grows between primitive forebrain and the stomodaeum stomodaeum Frontonasal process gets divided into median nasal process and two lateralSinuses open into the nasal cavity through openings in the lateral wall just under the middle turbinate, and the tear duct drains tears that pass down from the eyes, through an opening in the lateral wall just under the inferior turbinate




Nose And Paranasal Sinus




Pin On Glandular Odontogenic Cysts
Dermatomes Myotomes The Limbs Head and Neck Cardiovascular System Respiratory System Urinary System Reproductive System0513 · Log In The paranasal sinuses are airfilled extensions of the nasal cavity There are four paired sinuses named according to the bone in which they are located maxillary, frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid Each sinus is lined by a ciliated pseudostratified epithelium, interspersed with mucussecreting goblet cellsParanasal sinuses are a group of four paired airfilled spaces that surround the nasal cavity The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes;
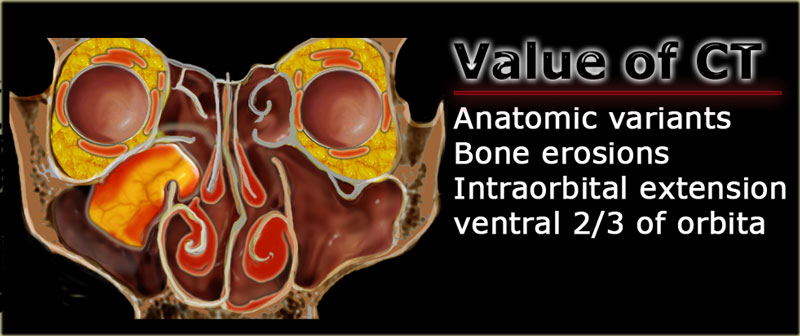



The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination




Surgical Views Paranasal Sinus Disease In Horses Vetfolio
· The size and specific anatomy of the frontal and sphenoid sinuses can be variable, and these sinuses may be absent in some animals 148,160 The frontal sinuses are connected to the nasal fossa via the nasofrontal opening, through which an ethmoidal turbinate extends Nasopharynx The nasopharynx is the portion of the pharynx dorsal to the hard and soft palatesA brief description of Anatomy of Nose & Paranasal air sinuses with respect to its size, internal features, blood supply, nerve supply, and clinical anatomy
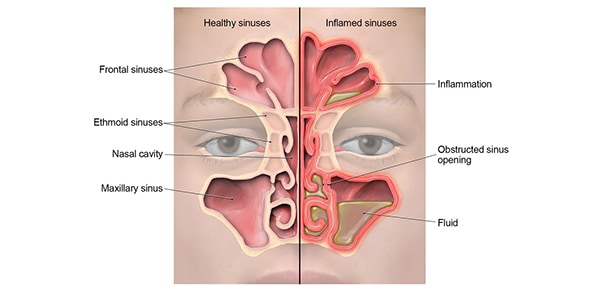



Sinus Infection Sinusitis Antibiotic Use Cdc
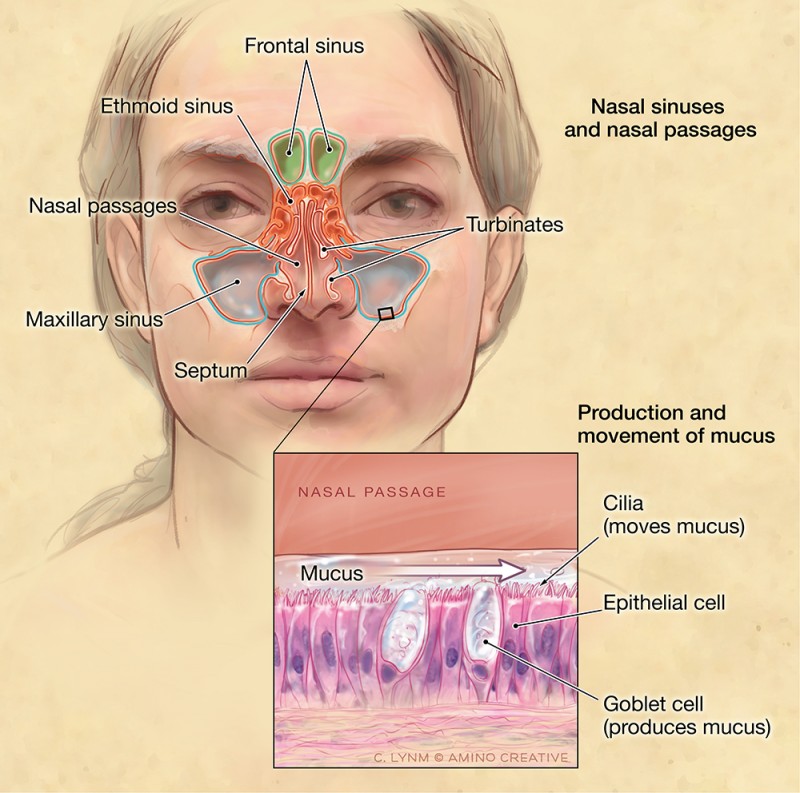



Dr Reuben Setliff Pioneer In Sinus Care
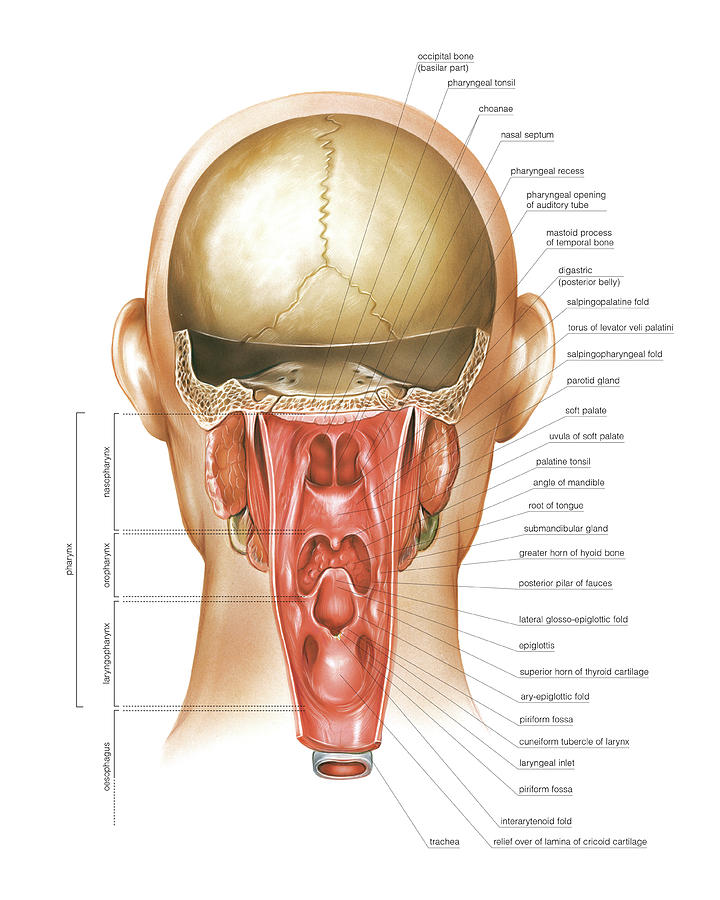



Paranasal Sinuses Photograph By Asklepios Medical Atlas



Anatomy Of The Sinuses Otolaryngology Houston




Nasal Cavity Nose Atlas Of Anatomy
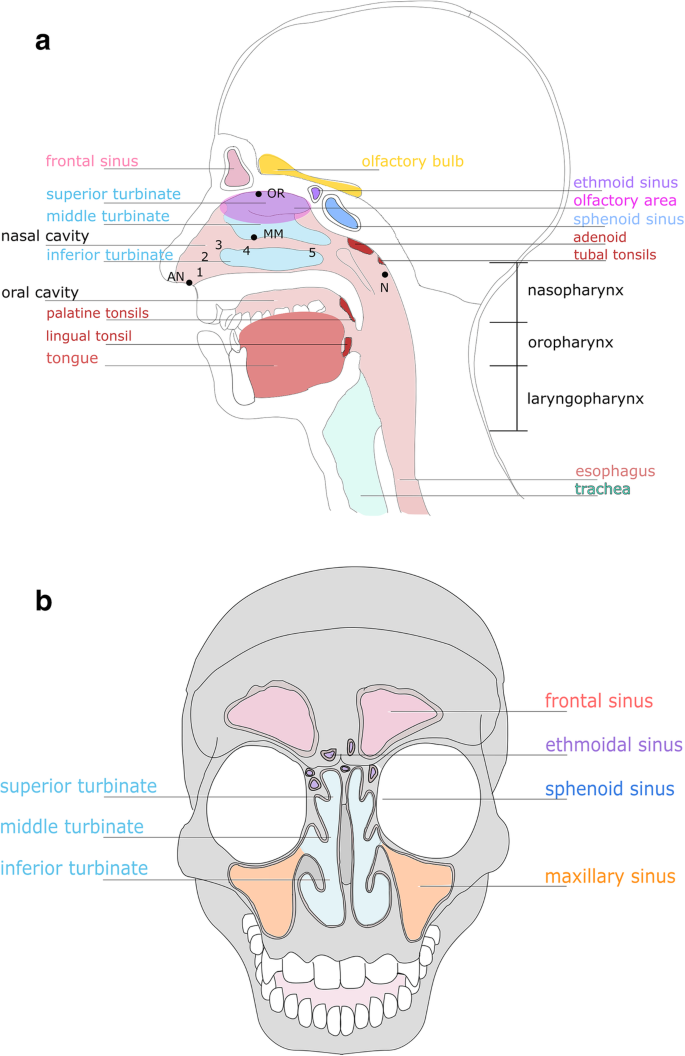



The Microbiome Of The Upper Respiratory Tract In Health And Disease Bmc Biology Full Text
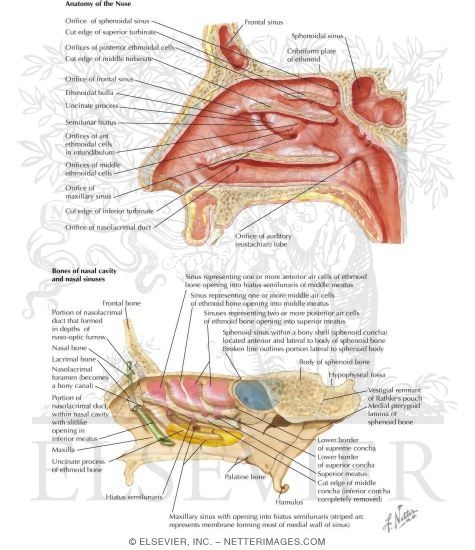



Drainage Of The Paranasal Sinuses And Associated Structures
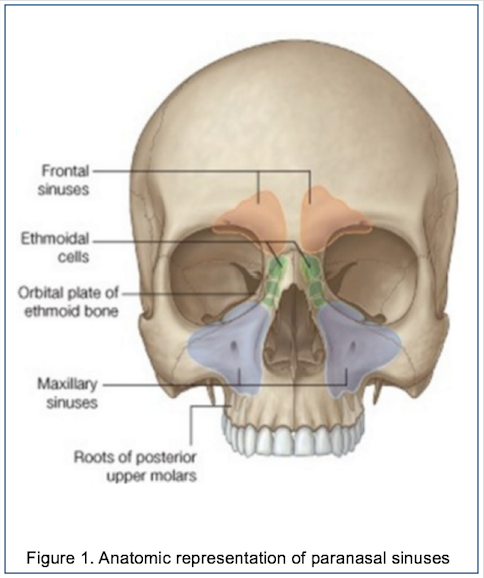



Epos C 2117
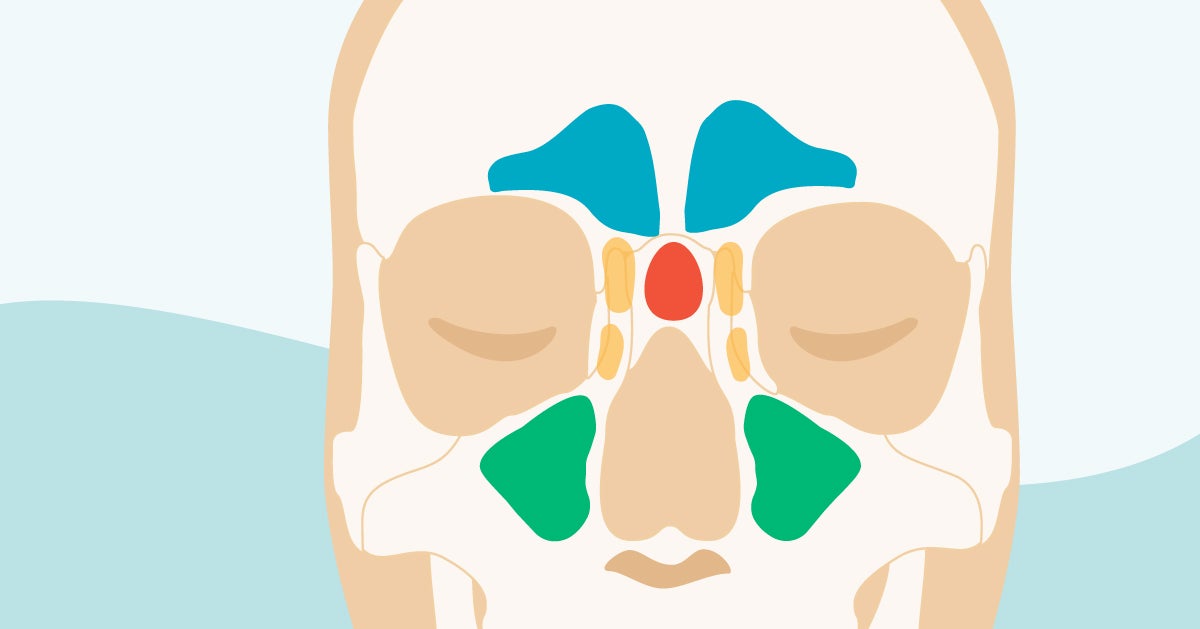



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures



1
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-paranasal-sinuses/972PC0nYOzlz7wqSgLmNA_sinus_frontalis_large_u9Vfozc0uUoMtc6KtIaUfw.png)



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
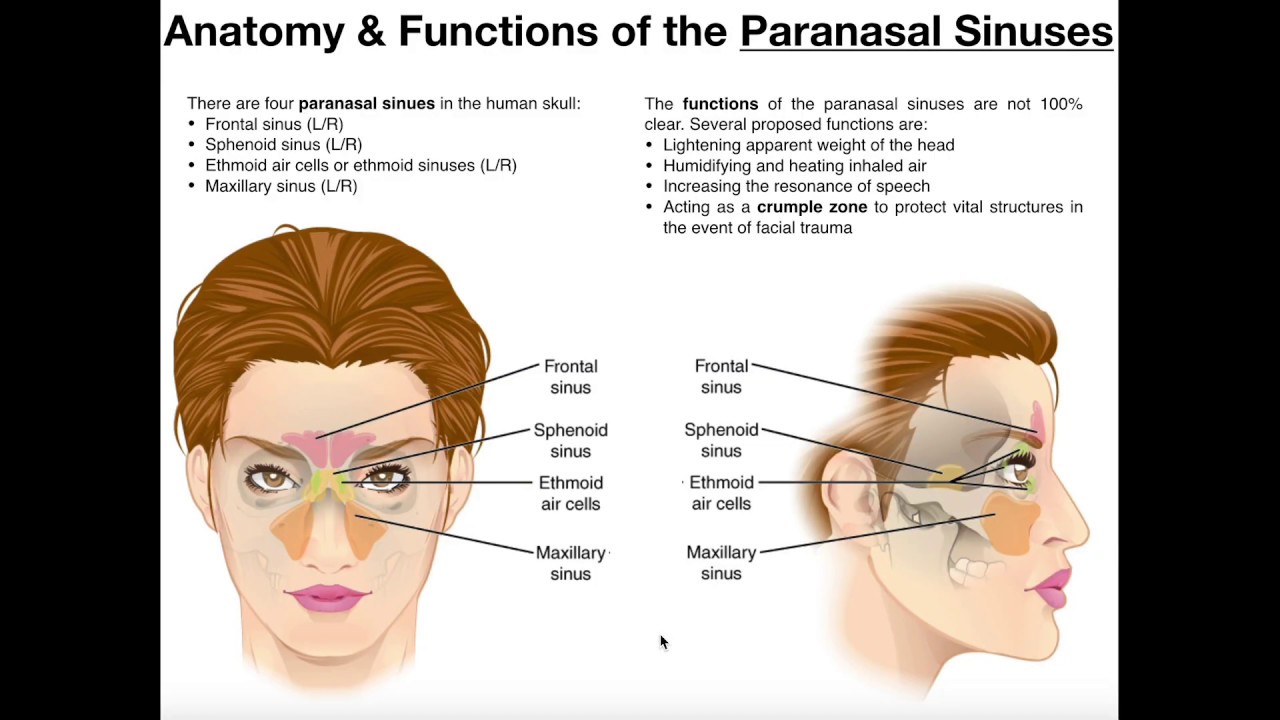



Anatomy And Functions Of The Paranasal Sinuses Youtube
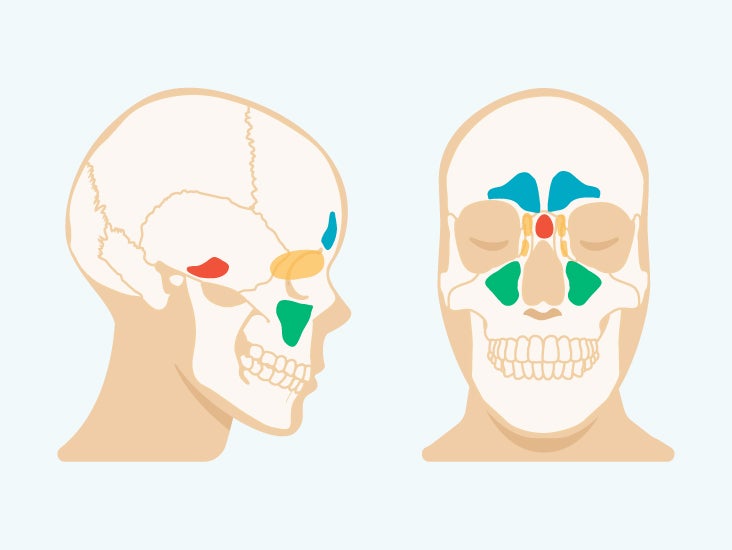



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures




Human Facial Anatomy Showing The Location Of Sinuses Entrance To The Download Scientific Diagram




Cancer Of The Nasal Vestibule Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Anterior Skull Base And Orbit Surgical Management Ento Key



Nasal Sinuses Anatomy Faculty Of Medicine




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia
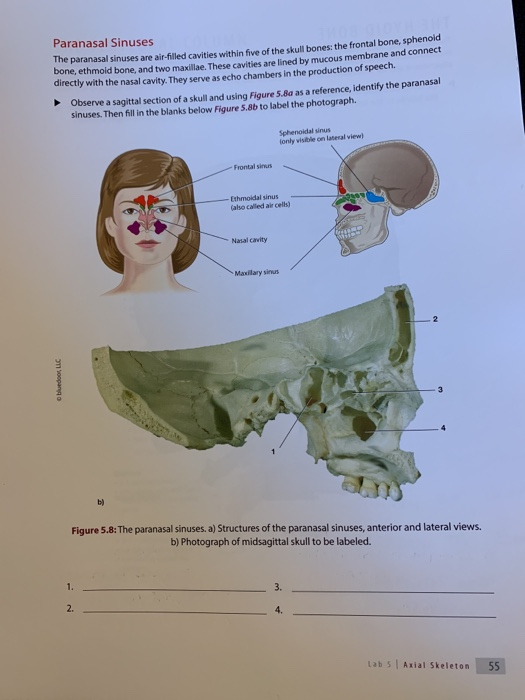



Paranasal Sinuses The Paranasal Sinuses Are Chegg Com
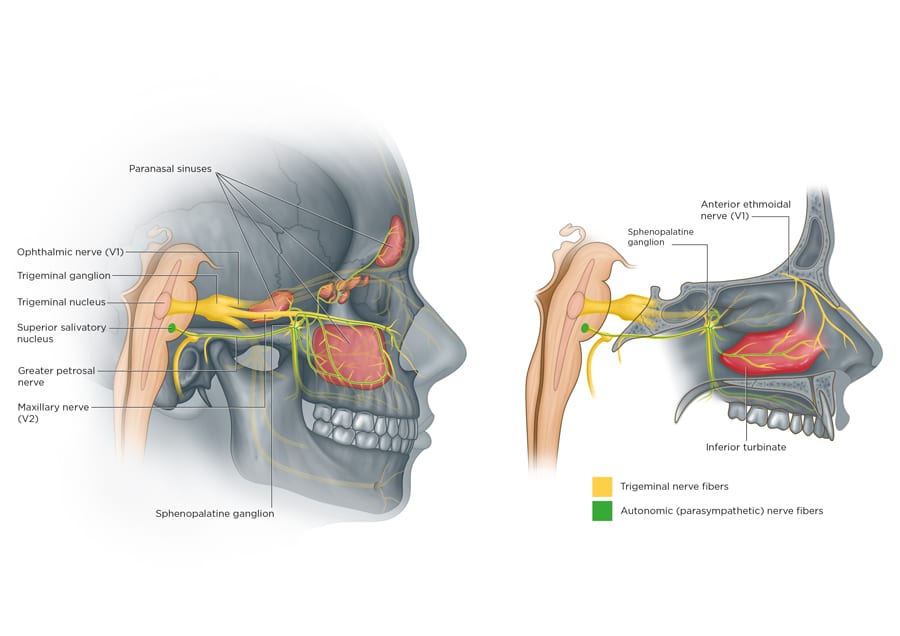



Sinus Migraine A Costly Blindspot In Medical Care Research Outreach




Ethmoid Sinus Ethmoid Bulla Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Nose People Anatomy Png Pngegg



Nasal Anatomy Uc Irvine Medical Center




Normal Anatomy Of The Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Mi Tec Medical Publishing




Pin On Paranasal Sinuses
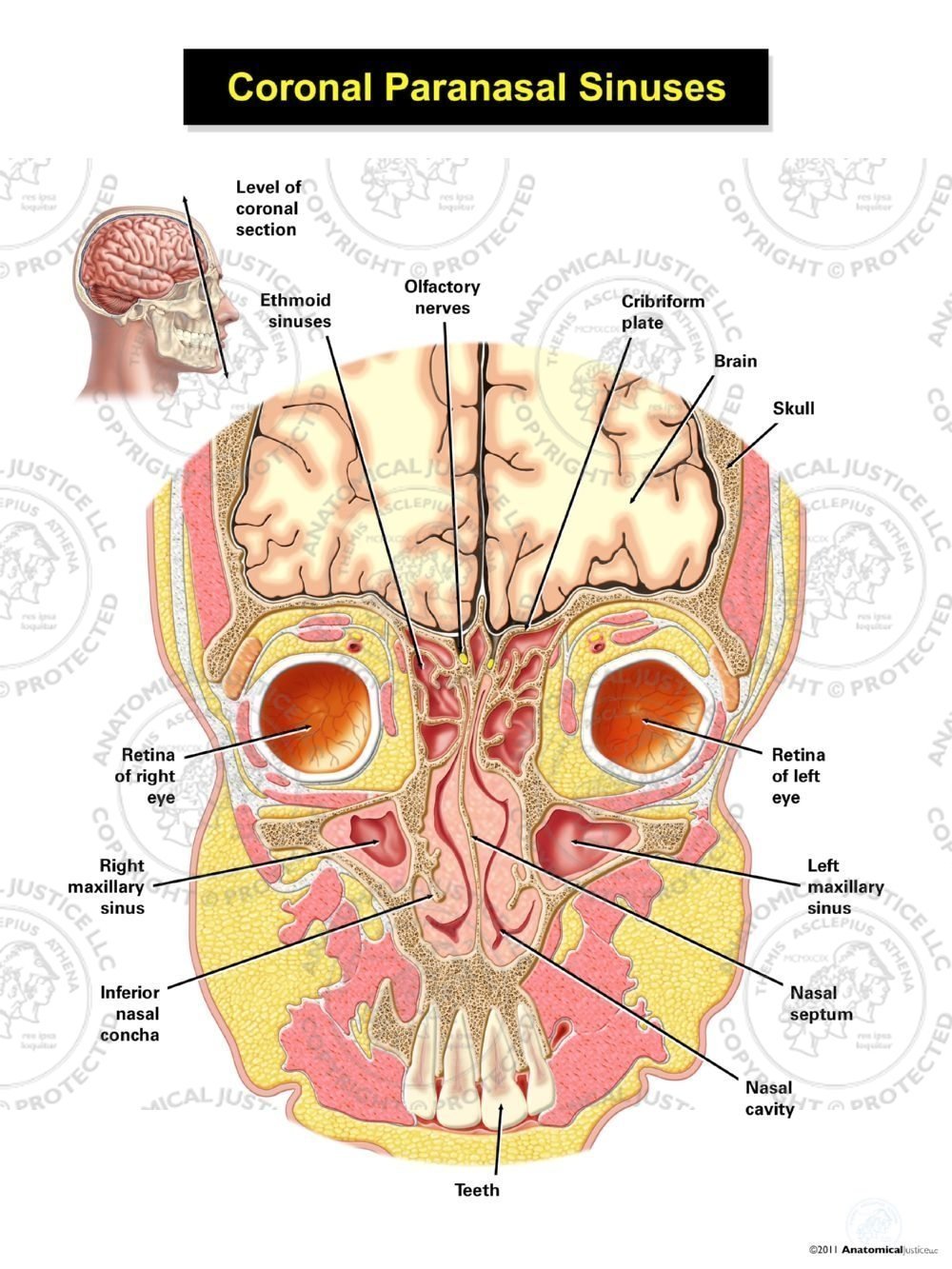



Coronal Paranasal Sinuses




What To Do About Sinusitis Harvard Health




Acute Sinusitis A Cost Effective Approach To Diagnosis And Treatment American Family Physician




The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Sciencekeys
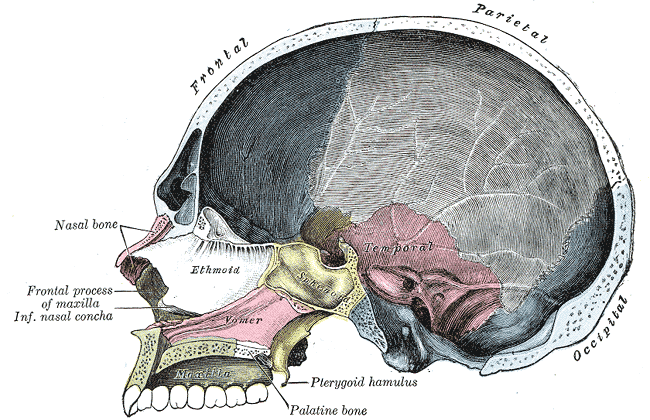



Sinus Cavities Paranasal Sinuses Location Anatomy Pictures Healthhype Com




Nasal Sinus Stock Vector Illustration Of Face Person
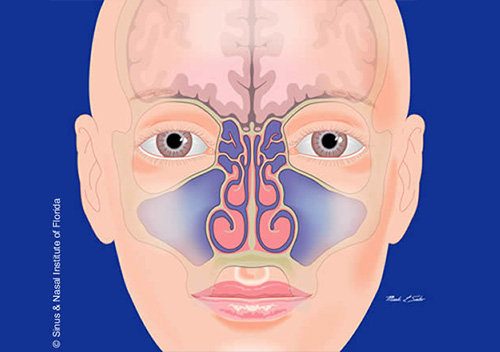



Sinus Nasal Institute Of Florida




The Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Canadian Cancer Society
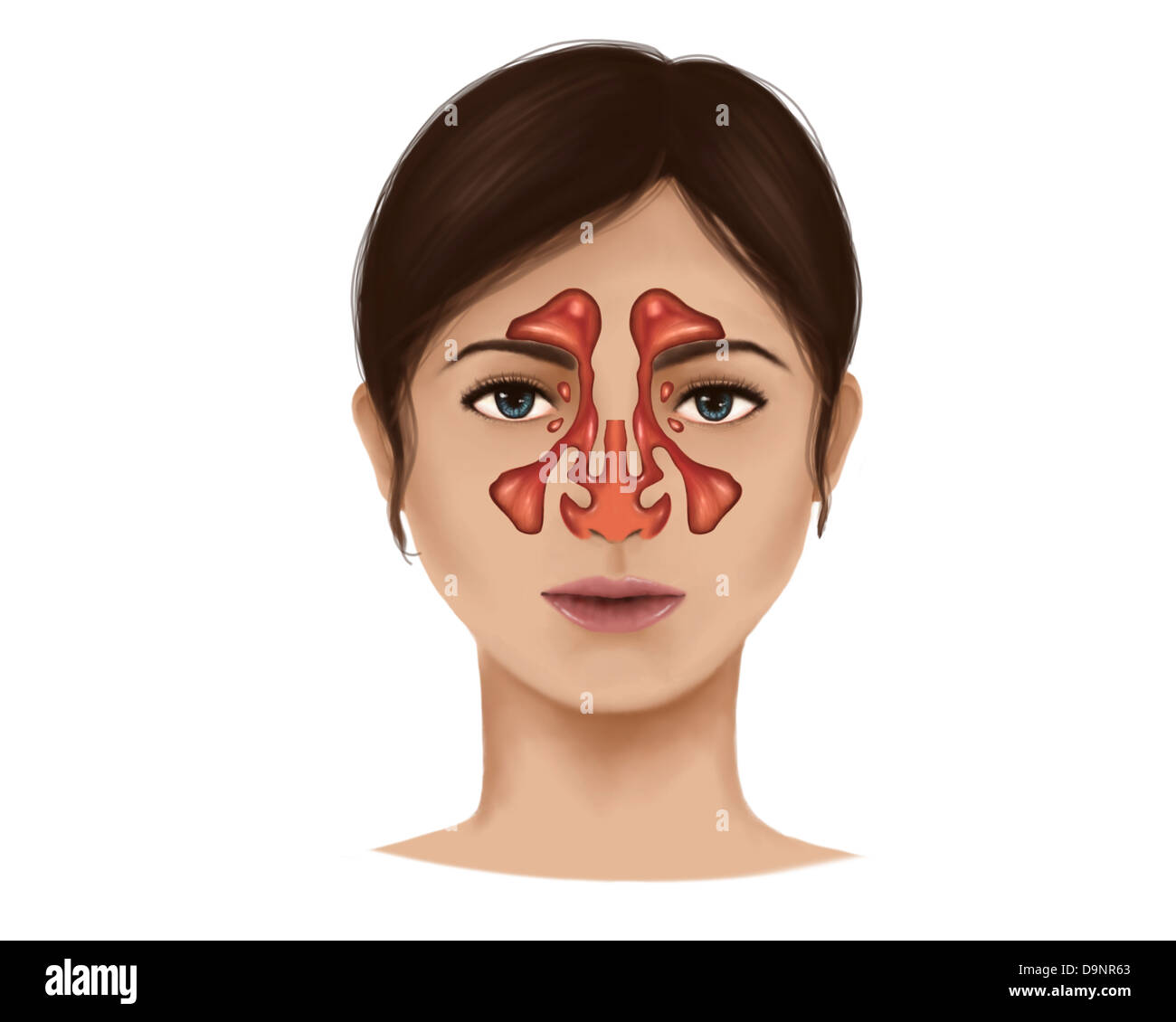



Anatomy Of Nasal Sinuses Stock Photo Alamy
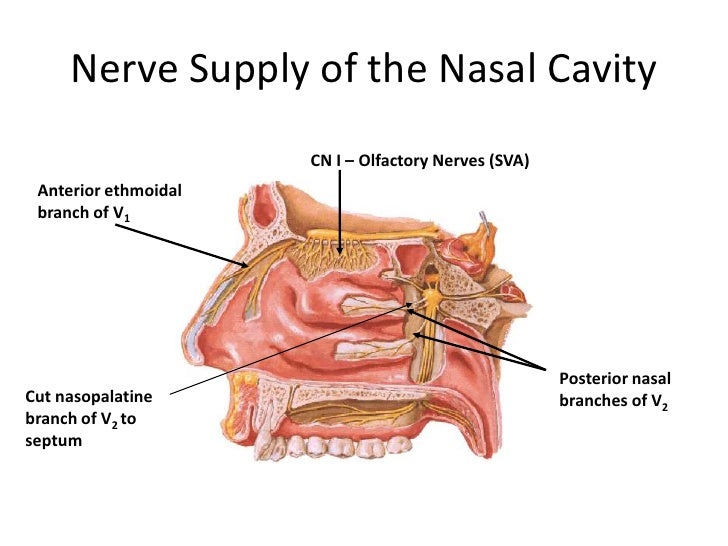



Anatomy Of Nasal Cavity Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Figure Paranasal Sinuses Frontal Sinus Ethmoid Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



Anatomy Of The Sinuses Otolaryngology Houston



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
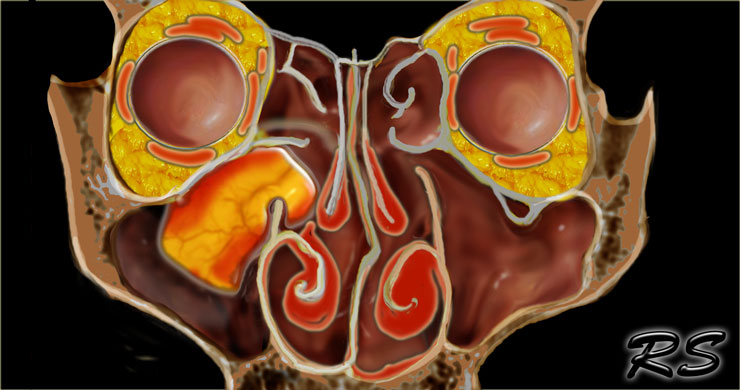



The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination




Paranasal Sinuses Diagram Quizlet




Clinical Anatomy Of Head Nasal Cavity Ppt Video Online Download




Pin On Health Tips




Sinus Pressure And Pain Specialist Spokane Washington Columbia Surgical Specialists
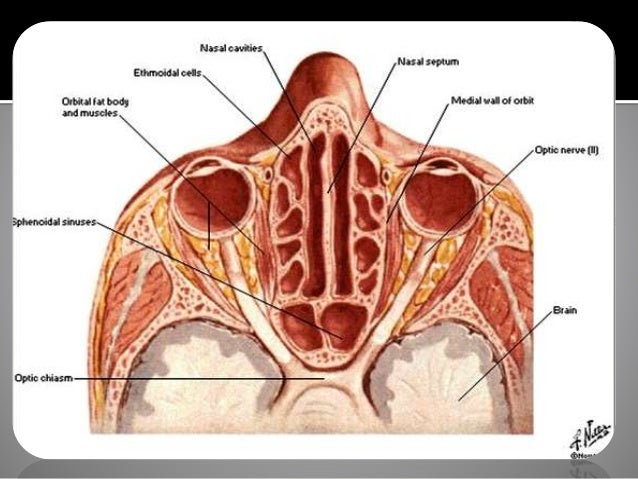



Anatomy Of Sinuses Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Tumours Of Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Col Shoaib



Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Radiologic Anatomy




Nose Sinus Ent




Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer Miami Cancer Institute Baptist Health South Florida




Sinusitis Healthy And Inflammation Nasal Sinus Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses 3d Illustration Showing Female With Highlighted Paranasal Sinuses Frontal Maxillary Ethmoid Canstock




Nose And Sinuses Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version




Nose Useful Notes On Human Nose And Para Nasal Sinuses Human Anatomy



Paranasal Sinuses Photograph By Asklepios Medical Atlas



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia



Acute Sinusitis Practice Essentials Background Anatomy




Evaluation Of The Patient With Nasal And Pharyngeal Disorders Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Merck Manuals Professional Edition
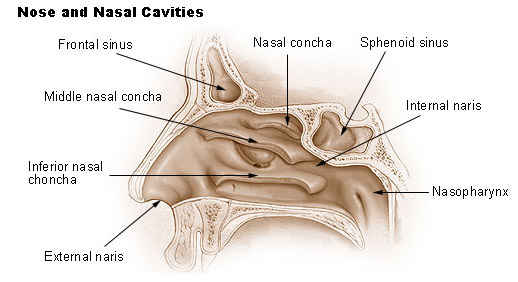



Seer Training Nose Nasal Cavities Paranasal Sinuses



The Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Applied Anatomy And Examination




Dr Pasha About Us Snoring Sinus Allergy Houston Sleep Center




Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Youtube
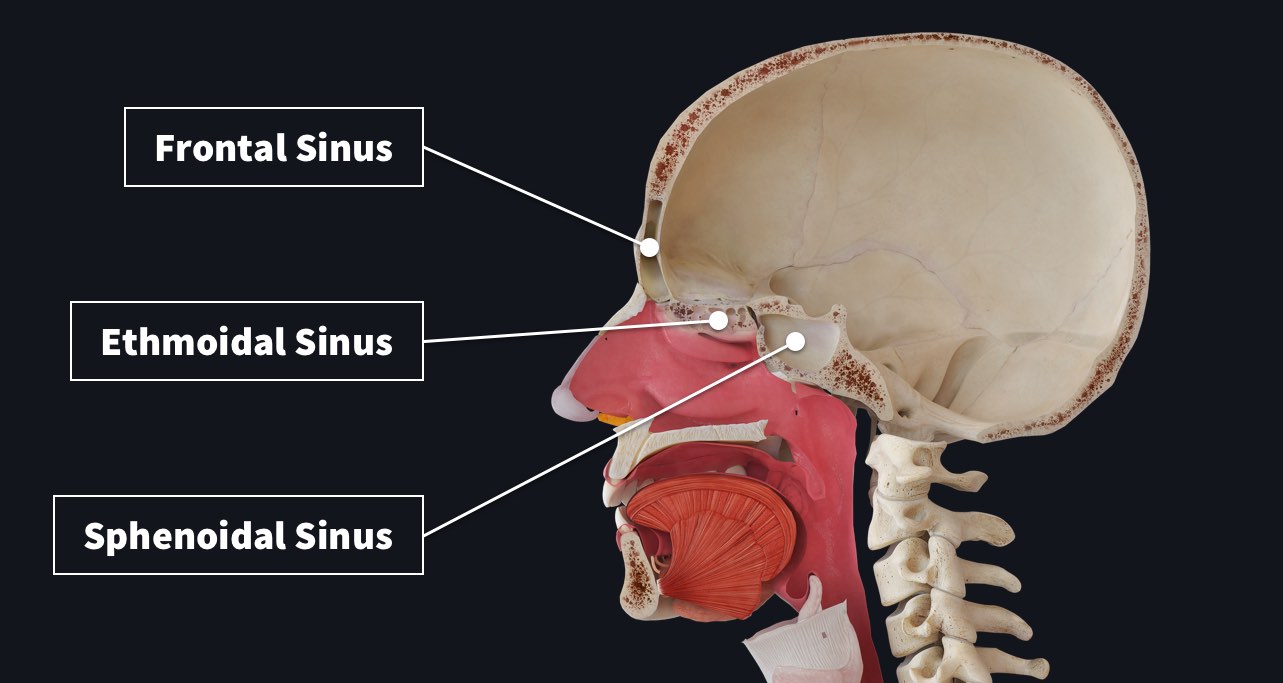



Paranasal Sinuses Complete Anatomy



Paranasal Air Sinuses Location Functions Relations And Applied Anatomy Qa




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Paranasal Sinus Anatomy Uptodate
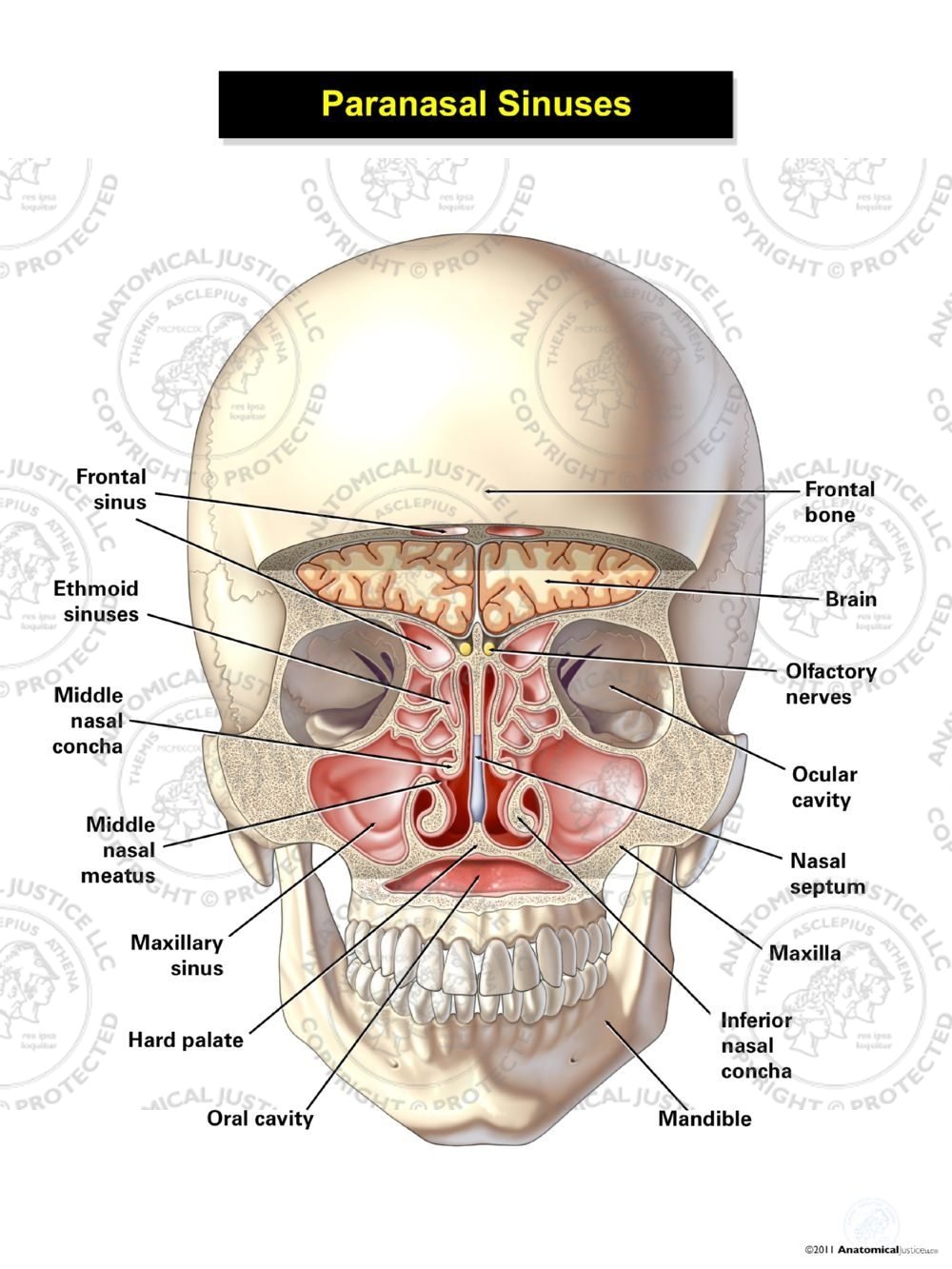



Paranasal Sinuses Illustration Anatomical Justice




Anatomy Model Nose With Paranasal Sinuses




Nasal Anatomical Model Anatomy Of Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Of Frontal Sinus Turbinate Mucosa Artery Olfactory Neural Model Aliexpress
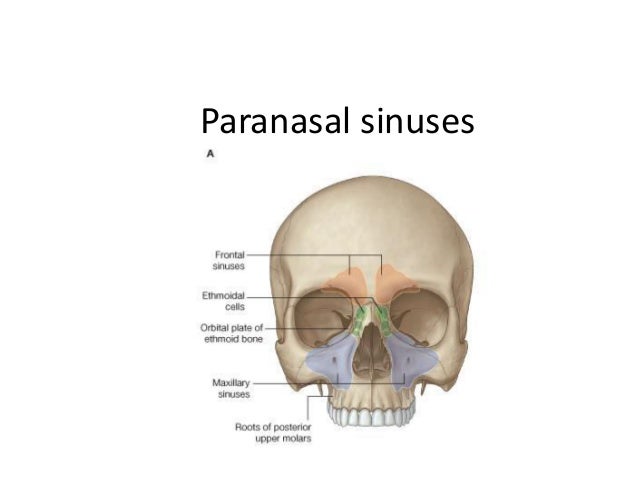



Paranasal Sinuses




Figure Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses Spaces Between The Bones Around The Nose Pdq Cancer Information Summaries Ncbi Bookshelf




Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses 3d Illustration Showing Male With Highlighted Paranasal Sinuses Frontal Maxillary Ethmoid Canstock




Paranasal Sinuses And Nose Anatomy




Sinus Anatomy Hd Stock Images Shutterstock



1
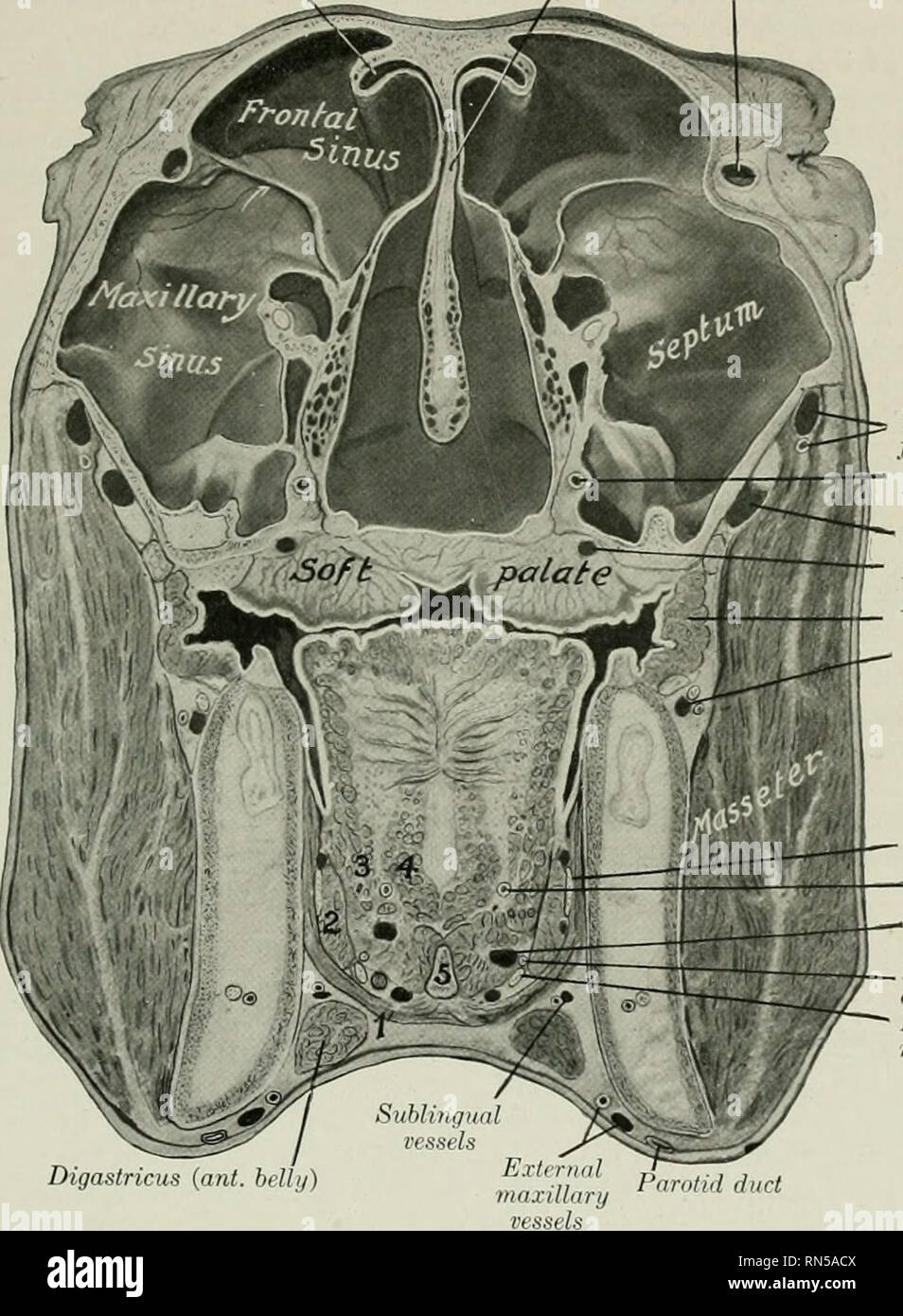



Paranasal Sinuses High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




2 Anatomy Of Nasal Sinuses Download Scientific Diagram



3
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10270/Paranasal_Sinuses.png)



Schwannoma Of The Nasal Cavity Clinical Case Diagnosis Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/nasal-cavity/FMVkU1Iob6HmAesgRBRQQ_Nasal_and_oral__part__cavities.png)



Nasal Cavity Anatomy Structure Parts Blood Supply Kenhub




Paranasal Sinuses Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
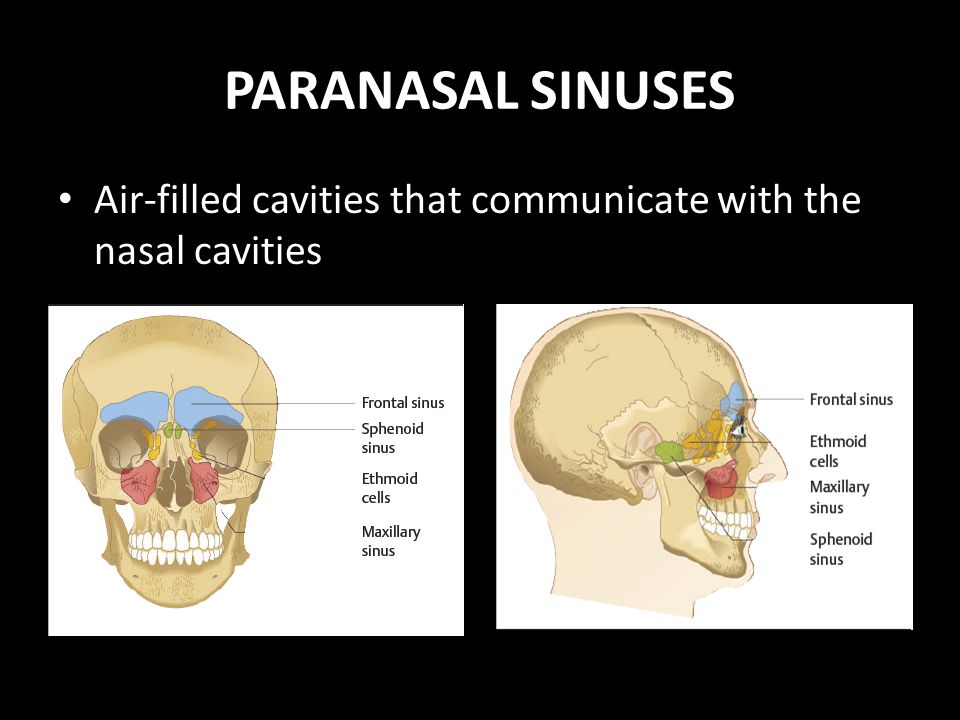



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Physiology And Diseases Ppt Video Online Download
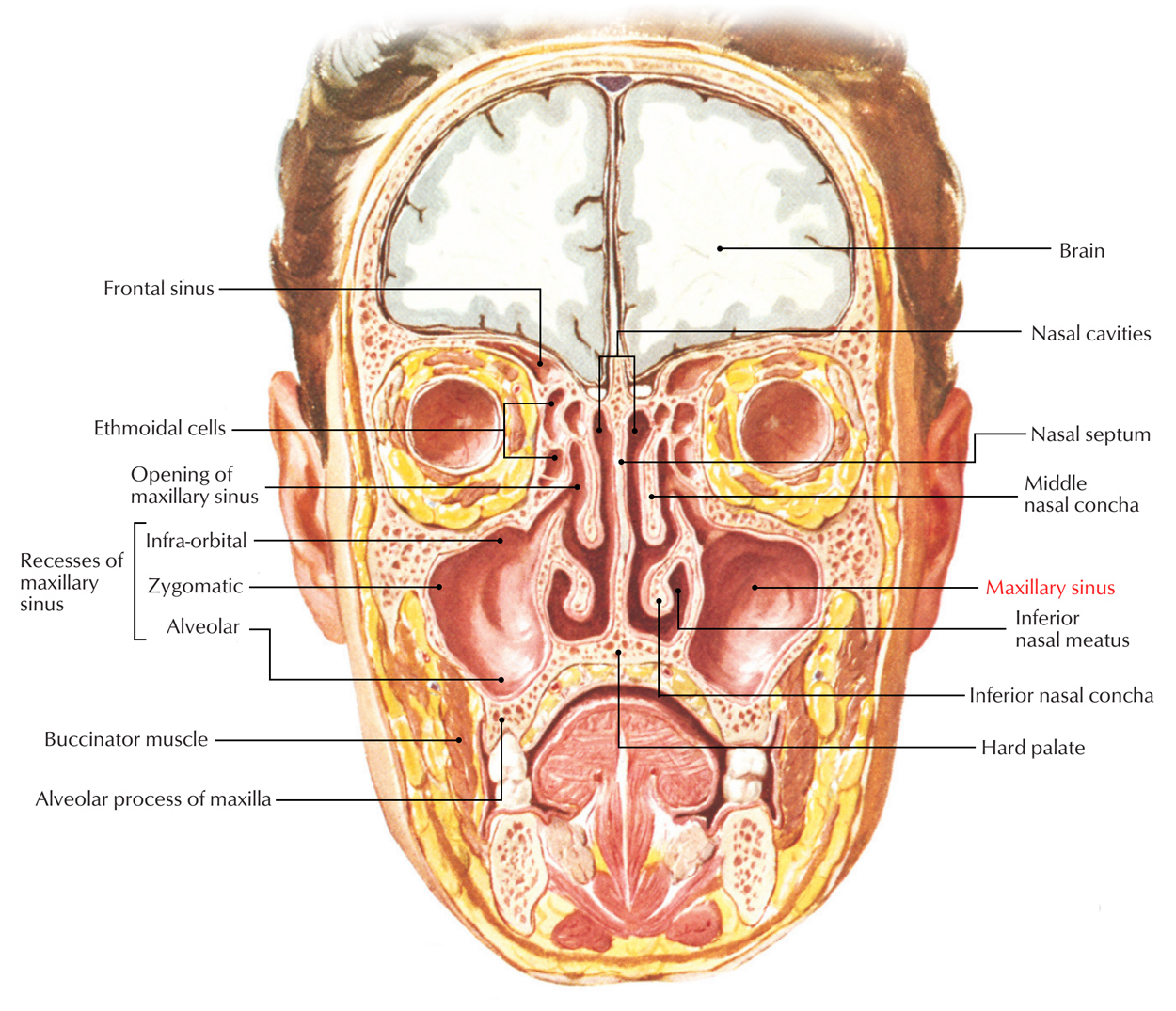



Maxillary Sinus Earth S Lab



コメント
コメントを投稿